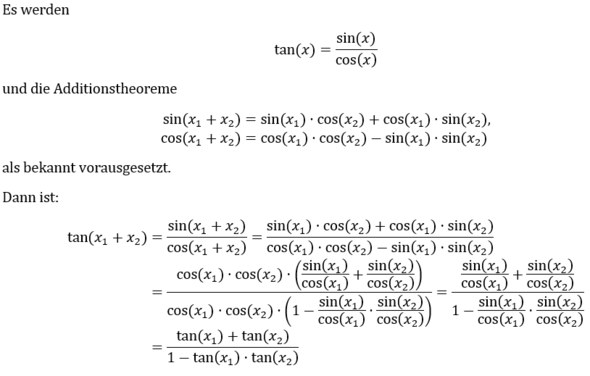Die Aufgabe lautet: Zeigen Sie Tan ( x1+x2) =tanx1+tanx2/1-tanx1*tanx2?
3 Antworten
Benutze:
e^(ix) = cos(x) + i*sin(x)
Damit folgt:
e^(i(x1 + x2)) = e^(ix1) * e^(ix2) = (cos(x1) + i*sin(x1)) * (cos(x2) + i*sin(x2))
Damit folgern wir die folgenden Additionstheoreme:
cos(x1 + x2) = cos(x1)cos(x2) - sin(x1)sin(x2)
sin(x1 + x2) = cos(x1)sin(x2) + cos(x2)sin(x1)
Damit folgt:
tan(x1 + x2) =
= (cos(x1)sin(x2) + cos(x2)sin(x1))/(cos(x1)cos(x2) - sin(x1)sin(x2))
Ausklammern von cos(x1)cos(x2) im Zähler liefert:
= (sin(x2)/cos(x2) + sin(x1)/cos(x1))*cos(x1)cos(x2)/(cos(x1)cos(x2) - sin(x1)sin(x2))
Nun Klammern wir aus dem Nenner cos(x1)cos(x2) aus:
= (sin(x2)/cos(x2) + sin(x1)/cos(x1))*cos(x1)cos(x2)/[ {cos(x1)cos(x2)}*(1 - sin(x1)sin(x2)/(cos(x1)cos(x2))) ]
Da nun im Zähler und Nenner der Faktor cos(x1)cos(x2) steht folgt durch kürzen unter der Bedingung: |cos(x1)cos(x2)| > 0
= (sin(x2)/cos(x2) + sin(x1)/cos(x1))/(1 - sin(x1)sin(x2)/(cos(x1)cos(x2)))
Benutzen der Definitionsgleichung für den Tangens: tan(x) = sin(x)/cos(x) ; liefert uns damit final:
= (tan(x2) + tan(x2))/(1 - tan(x1)*tan(x2))
Wir erhalten somit die gesuchte Identität:
tan(x1 + x2) = (tan(x2) + tan(x2))/(1 - tan(x1)*tan(x2))
unter der Bedingung: |cos(x1)cos(x2)| > 0
Eine Option wäre:
tan(a + b) = sin(a + b) / cos(a + b)
Ab hier die Additionstheoreme anwenden.
Dann wieder in den tan zurückführen.
Viel Spaß ;)
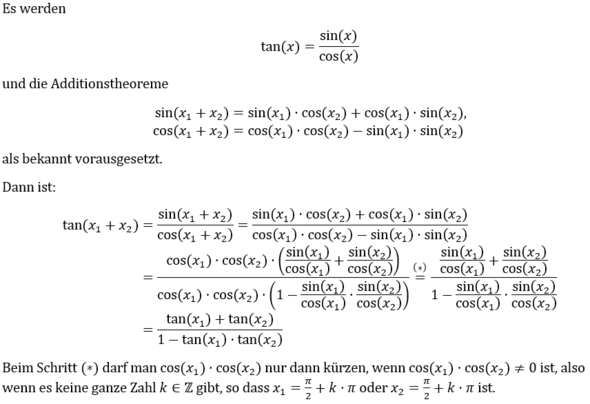
Eine Möglichkeit ist es, die Additionstheoreme für sin und cos auszunutzen, falls diese als bekannt vorausgesetzt werden.
Siehe: Bild im Anhang